A Coronary Angiogram (CAG) is a crucial diagnostic technique used to evaluate heart health, particularly the blood vessels that supply the heart. It’s commonly recommended for individuals experiencing symptoms or risk factors for heart disease, such as chest pain, shortness of breath, or a family history of heart conditions. This article provides an overview of what a Coronary Angiogram is, how the procedure is performed, its benefits, and who should consider undergoing this test.
Table of contents
- What is Coronary Angiogram (CAG)?
- How Does a Coronary Angiogram (CAG) Work?
- Why Do You Need a Coronary Angiogram?
- Benefits of a Coronary Angiogram (CAG)
- Who Should Consider a Coronary Angiogram?
- Risks and Complications of a Coronary Angiogram (CAG)
- Post-Procedural Care After a Coronary Angiogram
- Coronary Angiography (CAG) Package at Praram 9 Hospital
- Conclusion
What is Coronary Angiogram (CAG)?
A Coronary Angiogram (CAG) is a diagnostic procedure used to visualize the coronary arteries, which supply blood to the heart. It is used to identify blockages or narrowing of the arteries, which can lead to heart disease. During the procedure, a small catheter is inserted into a blood vessel, typically through the groin or arm, and contrast dye is injected into the arteries. X-ray imaging is then used to capture detailed images of the heart’s blood vessels, enabling doctors to detect blockages or other abnormalities effectively.
Coronary Angiograms are often recommended for patients with experiencing symptoms such as chest pain, shortness of breath, or those who are at high risk for heart disease. It provides crucial information for diagnosing coronary artery disease (CAD) and helps doctors develop an appropriate treatment plan, such as balloon angioplasty, stent placement, or coronary artery bypass surgery (CABG).
How Does a Coronary Angiogram (CAG) Work?
The process of a Coronary Angiogram involves several steps:
- Patient Preparation: Before the procedure, the patient is advised to avoid eating or drinking for 4-6 hours. A medical history is reviewed, and any medications being taken are checked.
- Insertion of the Catheter: A catheter is inserted into either the femoral artery (in the groin) or the radial artery (in the wrist). Local anesthesia is used to numb the area.
- Injection of Contrast Dye: Contrast dye is injected into the coronary arteries to make them visible on X-ray images.
- Imaging: X-ray imaging captures real-time, moving images of the coronary arteries. The doctor evaluates these images to identify any narrowing or blockages.
The procedure is typically completed within 30 minutes to an hour, depending on the complexity of the case.
Why Do You Need a Coronary Angiogram?
A Coronary Angiogram (CAG) is performed for several important reasons:
- Diagnosing Heart Disease: It helps detect conditions such as coronary artery disease (CAD), where the coronary arteries become narrowed or blocked.
- Assessing Severity: Detailed imaging allow doctors to assess the severity of blockages and plan appropriate treatments.
- Treatment Planning: The results of the angiogram guide decisions on treatments like angioplasty (ballooning) or stent placement.
- Monitoring Results: For patients who have undergone heart interventions, a Coronary Angiogram helps assess the success of treatments and check for new blockages.
- Identifying Other Heart Conditions: It can also reveal other heart problems like heart valve issues or heart muscle abnormalities.
Benefits of a Coronary Angiogram (CAG)
- Accurate Diagnosis: Provides detailed, real-time images of the coronary arteries, allowing doctors to diagnose blockages or narrowing with precision.
- Immediate Treatment: In many cases, a Coronary Angiogram can be combined with treatment, such as balloon angioplasty or stent placement, to open up blocked arteries.
- Reduces Risk of Heart Attack: Early detection and treatment of blockages help prevent severe complications such as heart attacks or sudden cardiac arrest.
- Minimal Recovery Time: The procedure is minimally invasive, allowing for a faster recovery compared to traditional surgery.
- Emergency Use: CAG can be performed in emergency situations, such as during a heart attack, to immediately assess and treat life-threatening blockages.
Who Should Consider a Coronary Angiogram?
Doctors may recommend a Coronary Angiogram for individuals who:
- Experience chest pain, shortness of breath, or other symptoms suggestive of heart disease.
- Are at high risk for heart disease, including those with a family history of heart disease, high cholesterol, or high blood pressure.
- Have diabetes or other conditions that increase the risk of coronary artery disease.
- Are scheduled for heart surgery and need a pre-surgical evaluation of their heart’s blood vessels.
- Have previously undergone heart procedures and need follow-up evaluations to monitor your heart’s condition.
Risks and Complications of a Coronary Angiogram (CAG)
While a Coronary Angiogram is a generally safe procedure, there are some risks to be aware of:
- Allergic Reaction: Some patients may have an allergic reaction to the contrast dye.
- Vascular Injury: The catheter insertion can occasionally cause injury to blood vessels.
- Blood Clots: There is a slight risk of blood clots forming at the catheter insertion site.
- Kidney Problems: The contrast dye may affect kidney function, especially in patients with pre-existing kidney conditions.
- Infection: As with any invasive procedure, there is a small risk of infection at the catheter insertion site.
Post-Procedural Care After a Coronary Angiogram
After undergoing a Coronary Angiogram, patients will need to follow these care guidelines:
- Rest and Observation: Patients may need to stay in the hospital for a day to monitor for complications.
- Wound Care: The insertion site must be kept clean and free from pressure to prevent infection or bleeding.
- Hydration: Drinking plenty of water helps flush the contrast dye from the body.
- Activity Limitations: Patients should avoid strenuous activities for a few days after the procedure.
- Follow-up Appointments: Regular check-ups are necessary to monitor heart health and any further treatment.
Coronary Angiography (CAG) Package at Praram 9 Hospital
Praram 9 Hospital offers a comprehensive Coronary Angiography (CAG) package at an affordable price of 55,000 THB (excluding room charges). This essential diagnostic procedure assesses the health of coronary arteries, identifying potential blockages or narrowing that may lead to heart conditions. By detecting issues early, the hospital ensures timely treatment to safeguard your cardiovascular health.
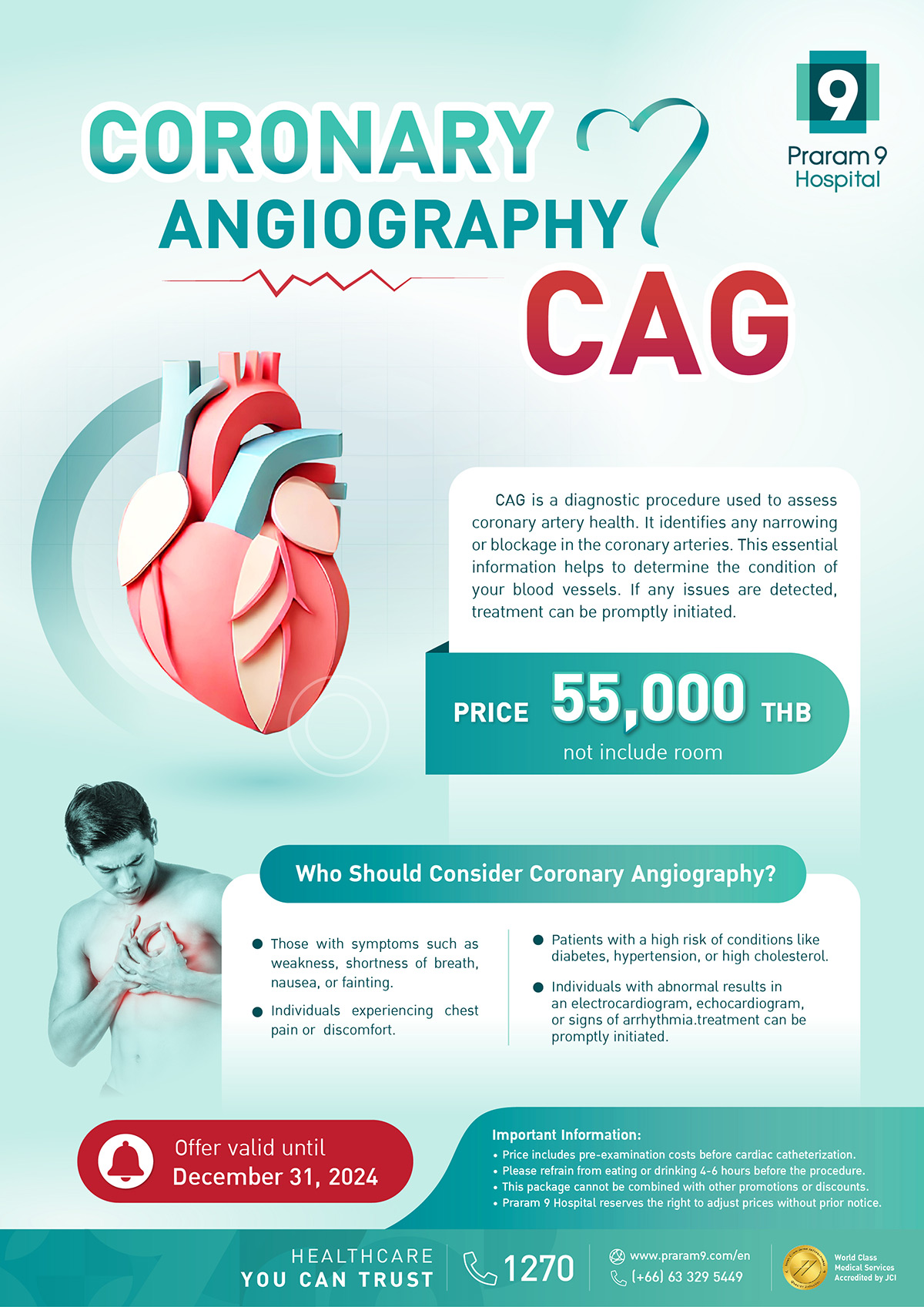
* This package is available until December 31, 2024. Take advantage of this opportunity to prioritize your heart health with trusted care from Praram 9 Hospital.
Why Choose Praram 9 Hospital for Your CAG?
- World-Class Healthcare: Praram 9 Hospital is accredited by JCI (Joint Commission International), guaranteeing high-quality standards and patient safety.
- Advanced Technology: State-of-the-art medical equipment for precise diagnosis and treatment.
- Expert Team: Experienced cardiologists and healthcare professionals dedicated to your well-being.
- Comprehensive Services: The package includes pre-examination costs before cardiac catheterization.
Conclusion
A Coronary Angiogram (CAG) is an essential diagnostic tool for detecting and treating heart disease. It provides detailed images of the coronary arteries, enabling doctors to assess the severity of any blockages and determine the most appropriate treatment plan. While the procedure carries some risks, its benefits far outweigh the potential complications, particularly in diagnosing and managing heart disease. Regular screenings and timely interventions can help prevent serious heart conditions, improving overall health outcomes.
For more information or urgent, please contact
TEL: 1270 (Local) or +662 202 9999
Email: [email protected]
You can consult a doctor from anywhere through video calls.






