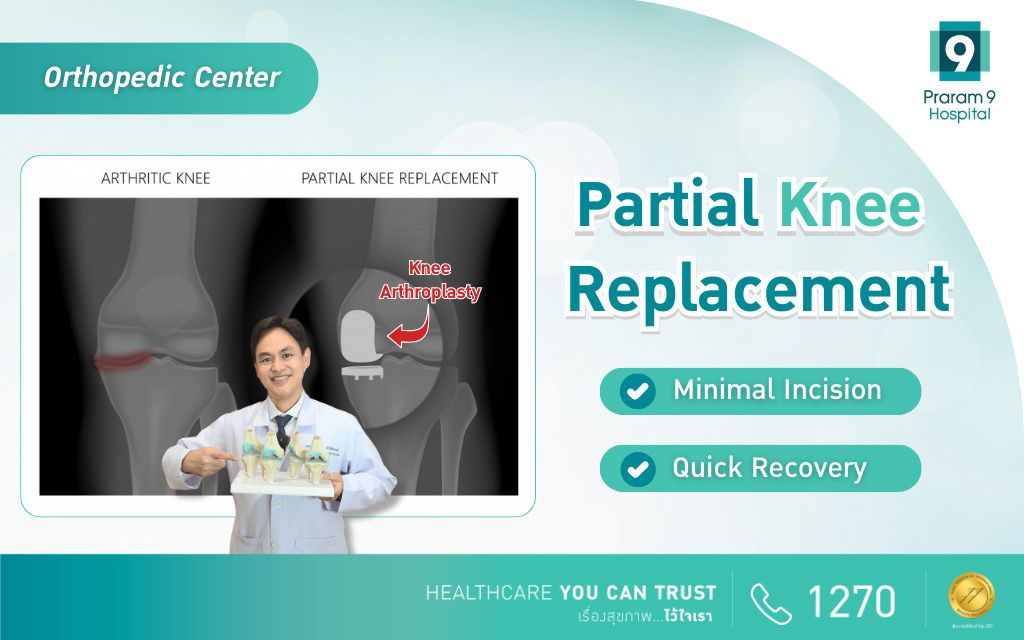
Health Articles
Knowledge
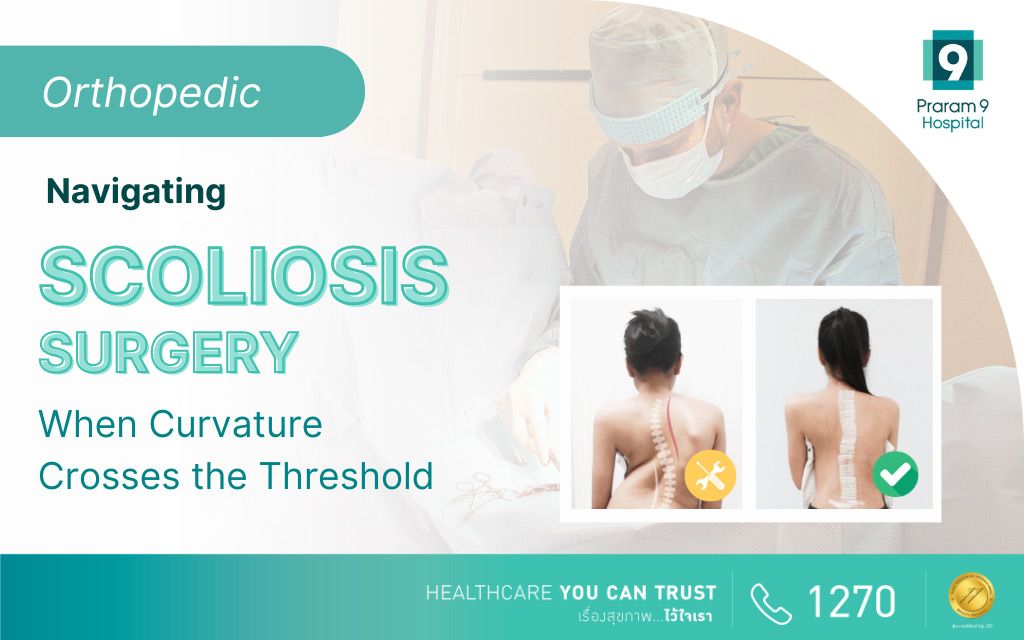
Navigating Scoliosis Surgery When Curvature Crosses the Threshold
Introduction:
Scoliosis is a medical condition characterized by an abnormal curvature of the spine, often be diagnosed during adolescence. While many cases can be managed through non-surgical interventions such as bracing and physical therapy, severe scoliosis may require surgical intervention to correct the spinal deformity. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the various aspects of scoliosis surgery, including its indications, surgical procedures, recovery process, and potential risks.
Indications for Scoliosis Surgery:
Scoliosis surgery is typically recommended in cases that the spinal curvature exceeds a certain degree and continues to progress despite non-surgical interventions. The decision to undergo surgery is a collaborative effort between the patient, their family, and the healthcare team. Indications for scoliosis surgery may include:
- Severity of Curvature: Surgery is often considered when the spinal curvature reaches or exceeds 40-50 degrees.
- Progression of Curvature: If the curvature is rapidly progressing, especially during the adolescent growth spurt, surgery may be recommended to prevent further deformity.
- Pain and Discomfort: Persistent pain and discomfort that do not respond or fail conservative treatments may indicate the need for surgical intervention.
Types of Scoliosis Surgery:
There are various surgical approaches to treat scoliosis, and the choice of procedure depends on factors such as the severity and location of the curvature. Common surgical techniques include:
- Spinal Fusion: This is the most common type of scoliosis surgery. It involves fusing the vertebrae together with the use of bone grafts and sometimes metal rods to straighten and stabilize the spine.
- Growing Rods: This approach is often used in pediatric cases where the spine is still growing. Adjustable rods are implanted are allowed for lengthening as the child grows.
- Vertebral Body Tethering (VBT): A more recent development, VBT involves attaching a cord to the spine, allowing for controlling movement and growth while maintaining stability.
The Scoliosis Surgery Process:
Scoliosis surgery is a complex procedure that requires careful planning and skilled execution. The surgical process typically involves the following key steps:
- Preoperative Evaluation: the thorough assessment of the patient’s overall health, spinal condition, and any potential risks is conducted.
- Surgery Day: The patient is administered general anesthesia, and the surgical team begins the process of correcting the spinal curvature using the chosen surgical technique.
- Postoperative Care: After surgery, patients are closely monitored in the recovery room before being transferred to a hospital room. Pain management, wound care, and physical therapy are integral components of postoperative care.
Recovery and Rehabilitation:
Recovery from scoliosis surgery is a gradual process that requires patience and commitment. Key aspects of the recovery and rehabilitation phase include:
- Hospital Stay Duration: The duration of the hospital stay varies but is typically around 4-7 days. During this time, healthcare professionals monitor the patient’s condition and provide necessary support.
- Physical Therapy: Rehabilitation involves physical therapy to regain strength, flexibility, and mobility. Patients will learn exercises and techniques to support their spine and improve overall function.
- Follow-up Care: Regular follow-up appointments with the surgical team are crucial for monitoring the healing process, addressing any concerns, and adjusting the treatment plan as needed.
Potential Risks and Complications:
While scoliosis surgery is generally safe, like any surgical procedure, it carries some risks and potential complications. These may include:
- Infection: Risk it occurs at the surgical site, although rare, but it needs to be concerned that requires vigilant postoperative care.
- Instrumentation Failure: Hardware such as rods or screws may fail or break, requiring additional surgery.
- Nerve Damage: In rare cases, surgery may lead to nerve damage, resulting in sensory or motor deficits.
Conclusion:
Scoliosis surgery is a significant and often necessary step in the treatment of severe spinal curvature. With advancements in surgical techniques and postoperative care, the majority of patients experience successful outcomes and improved quality of life. If you or a loved one is considering scoliosis surgery, it is essential to consult with a qualified healthcare professional to determine the most appropriate treatment plan based on individual circumstances. Remember, informed decision-making and proactive postoperative cares are integral to a successful recovery journey.