Health Articles
Knowledge
What is the thyroid gland? What are thyroid diseases? How can it be treated?


Hello, my name is Dr. Thanyawat Sasanakiatkul. I am a specialist in Thyroid diseases and parathyroid surgery. Today I will be explaining to you about the thyroid glands and thyroid diseases so both patients and relatives can have a broader picture and understanding of it.
What is the thyroid gland? What are thyroid diseases? How can it be treated?
The thyroid is the largest endocrine gland in your body positioned in front of the trachea right in the middle on the neck under the Adam’s apple.
Thyroid gland diseases can be categories into 3 main groups:
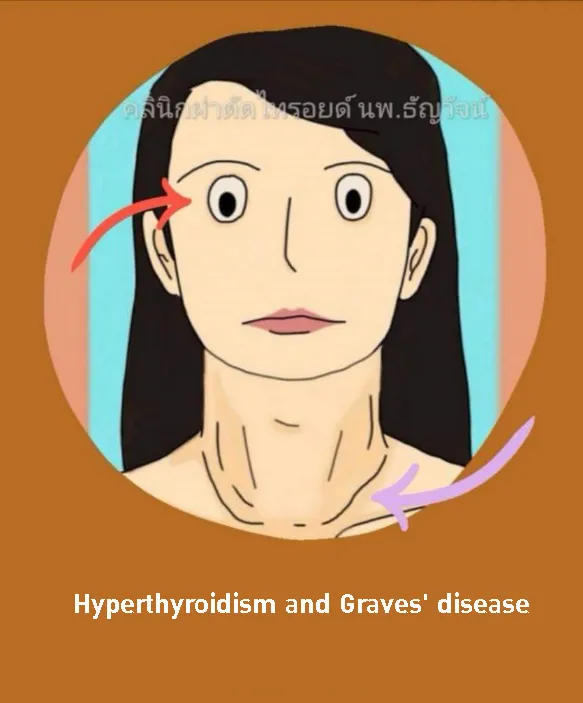
1. Hyperthyroid: a condition in where the thyroid over produces thyroid hormones.
Since there is an over production of hormones in the body, your whole body’s function will be affected directly. Symptoms includes heat flashes, easily irritated, fatigue, trembling hands, and no weight gain despite how much you eat. Diagnosis for hyperthyroid is easy, the level of hormones (FT3, FT4, and TSH) in blood will be measured to see if they are at the right levels.
The most common cause of Hyperthyroid is from Grave’s Disease which is an immune deficiency disease causing the body to produce a higher level of hormones than normal. Certain drugs and medication can cause thyroid poisoning or toxicity as well and alter the level of hormones in the body.
The cause of the over production of hormones has to be treated in order to treat hyperthyroid which causes thyroid poisoning to the body. Treatments includes antithyroid medication or thyroid surgery.
2. Hypothyroid: a condition where your thyroid hormones in the body are lower than normal. The diagnosis is the same diagnosis for hyperthyroid where the hormones level in your blood are measured. Symptoms of thyroid hormone deficiency are obesity, fatigue, constant drowsiness, constipation, and slow heart rate.
Causes of hypothyroidism are mainly due to chronic inflammation from autoimmune thyroiditis, or from chronic Hashimoto’s thyroiditis. These can be treated by supplying medication to increase thyroid hormones in the body.
Brain disorders that inhibit the secretion of thyroid hormones. This can also be treated by supplying thyroid hormones medication.
In cases where there is an inflammation and the thyroid is enlarged, the thyroid gland will need to be removed to prevent it from pressing on nearby organs.
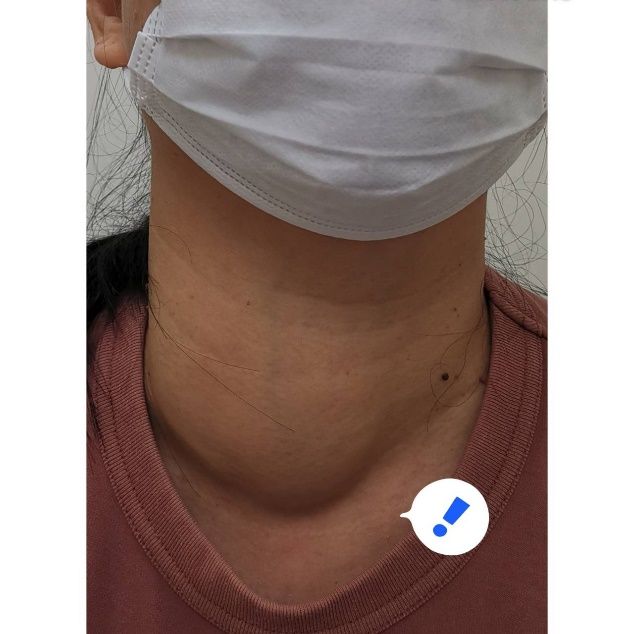
3. Cancerous and non-cancerous thyroid tumors (malignant and benign thyroid nodule).
Most of the time the hormone blood level of patients will be normal as tumors cannot produce hormones. Most patients do not have any other symptoms except for enlarge lumps around the thyroid area. These tumors will continue to grow and press on the trachea and esophagus making it very difficult to breathe and swallow.
Patients with enlarge lumps can look in the mirror and swallow saliva and see if the lump moves up and down with the movement of their swallowing. If the tumor is still very small, a neck ultrasound will be done for diagnosis.
There are many different types of thyroid tumor, the most common being Papillary thyroid cancer. This is most manageable when found early which reduces the risk of the cancer spreading, and the risk of recurrence. Patients with thyroid tumor require surgery as soon as possible to prevent the cancer spreading to the lymph nodes or other organs in the body. Most people can recover from thyroid cancer if they receive the correct treatment early by a professional. It is important to consult and thyroid specialist surgeon for the surgery to be most effective.
Package
About the Author