Health Articles
Knowledge
Understanding Spinal Nerve Compression and Treatment Options
RATTALERK ARUNAKUL,M.D.
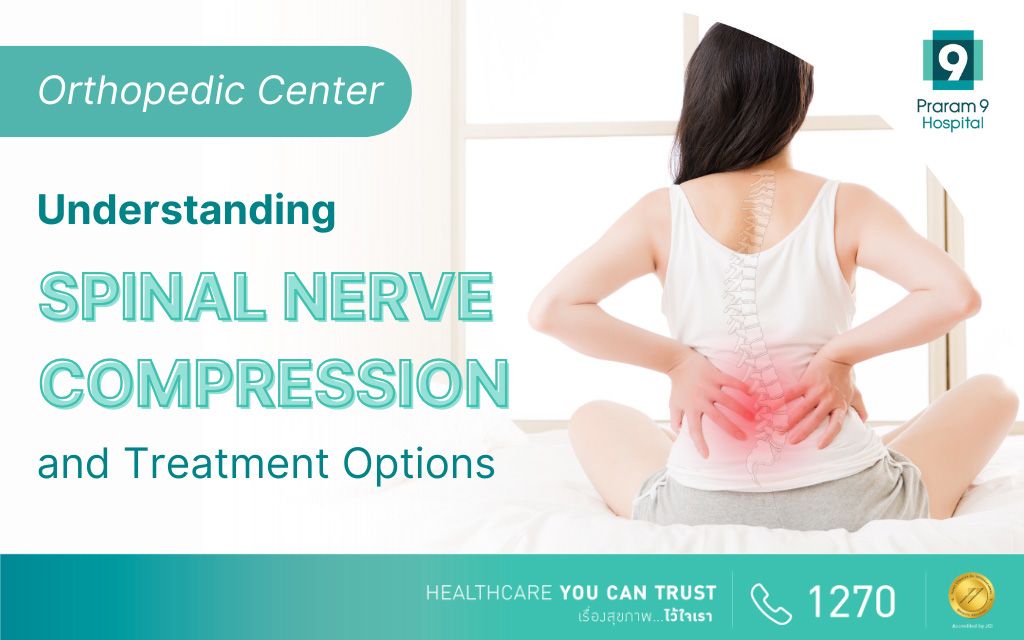
Find relief from back pain and discomfort with specialized spinal health care. Learn about nerve compression issues and treatment options. Contact us for expert diagnosis and personalized spinal care plans.
Introduction
Spinal nerve compression is a common issue that can cause significant discomfort and pain. It can result from various factors, including injuries, improper posture, and degenerative conditions. This article will discuss the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for spinal nerve compression, emphasizing the importance of timely diagnosis and specialist consultation.
Table of contents
- What is Spinal Nerve Compression?
- Common Causes of Spinal Nerve Compression
- Symptoms of Spinal Nerve Compression
- Diagnosis and Evaluation of Spinal Nerve Compression
- Treatment Options of Spinal Nerve Compression
- Preventive Measures of Spinal Nerve Compression
- Conclusion
What is Spinal Nerve Compression?
Spinal nerve compression occurs when nerves in the spinal cord are compressed or pinched. This can lead to pain, numbness, and weakness, particularly in the back, neck, and limbs. The condition can significantly impact mobility and quality of life if not addressed promptly.
Common Causes of Spinal Nerve Compression
Several factors can contribute to spinal nerve compression, including:
- Herniated Discs: Discs that protrude and press on spinal nerves.
- Spinal Stenosis: Narrowing of the spinal canal that compresses nerves.
- Bone Spurs: Overgrowth of bone that can press on nerves.
- Injuries: Accidents or injuries to the spine.
- Poor Posture: Prolonged poor posture can lead to nerve compression.
- Degenerative Diseases: Conditions like arthritis that cause wear and tear on the spine.
Symptoms of Spinal Nerve Compression
Common symptoms include:
- Back or Neck Pain: Persistent pain in the back or neck.
- Numbness and Tingling: Sensations of numbness or tingling in the extremities.
- Weakness: Weakness in the arms or legs.
- Loss of Reflexes: Reduced reflexes in the affected areas.
- Difficulty Moving: Pain that worsens with movement.
Diagnosis and Evaluation of Spinal Nerve Compression
Proper diagnosis involves a thorough evaluation by a specialist, including:
- Medical History: Detailed history of symptoms and past injuries.
- Physical Examination: Assessment of posture, reflexes, and muscle strength.
- Imaging Tests: MRI, CT scans, and X-rays to visualize the spine and identify compression areas.
Treatment Options of Spinal Nerve Compression
Treatment for spinal nerve compression depends on the severity of the condition and includes:
- Medications: Pain relievers, anti-inflammatory drugs, and muscle relaxants.
- Physical Therapy: Exercises to strengthen the spine and improve flexibility.
- Lifestyle Modifications: Posture correction and ergonomic adjustments.
- Injections: Corticosteroid injections to reduce inflammation and pain.
- Surgery: In severe cases, surgical options like laminectomy or discectomy may be necessary to relieve compression.
Preventive Measures of Spinal Nerve Compression
To prevent spinal nerve compression, consider the following tips:
- Maintain Good Posture: Practice good posture, especially when sitting and standing.
- Regular Exercise: Engage in regular physical activity to strengthen the back and core muscles.
- Proper Lifting Techniques: Use proper techniques when lifting heavy objects to avoid injury.
- Ergonomic Adjustments: Ensure your work environment supports proper posture and reduces strain on the spine.
Conclusion
Spinal nerve compression can cause significant discomfort and impact daily life. Early diagnosis and treatment are crucial to managing symptoms and preventing further complications. The Spine Center at Praram 9 Hospital offers specialized care and advanced diagnostic services to help patients find the best treatment options. If you experience symptoms of spinal nerve compression, consult a specialist to discuss your condition and treatment plan.