Health Articles
Knowledge
Knee Osteoarthritis Surgery with Knee Replacement A Path to Improving Quality of Life and Becoming Active Again

Knees that have been used for a long time will inevitably deteriorate over time. Knee replacement surgery is one of the ways to restore quality of life for patients with knee osteoarthritis, allowing them to return to daily activities with improved function.
Key Takeaways
- Knee osteoarthritis surgery with knee replacement involves removing worn joint surfaces and replacing them with metal and high-quality materials, allowing the knee to function normally again.
- There are two types of knee replacement surgery: total knee replacement and partial knee replacement.
- Patients who require knee replacement surgery usually have severe knee osteoarthritis, such as severe knee pain in all positions, knee deformity, and symptoms that cannot be relieved with medication or physical therapy.
What Is Knee Osteoarthritis? Is It Only Found in the Elderly?
permanent structural changes in the bones around the knee joint. This results in pain and difficulty moving the knee, with symptoms progressively worsening if not properly treated.
Knee osteoarthritis is commonly found in people over the age of 55, as the knee joints have been used for many years and naturally deteriorate over time. However, younger individuals can also develop knee osteoarthritis depending on lifestyle factors. These include previous knee injuries, a history of meniscus tears, frequent kneeling or sitting cross-legged, and being overweight, all of which can accelerate joint degeneration. Knee osteoarthritis can also result from other conditions such as joint infections, rheumatoid arthritis, or gout.
How Severe Must Knee Osteoarthritis Be to Require Surgery?
Patients with knee osteoarthritis may need surgery if they experience the following:
- Severe knee pain that interferes with daily life
- Constant knee pain regardless of position
- Knee swelling, warmth, and redness indicating severe inflammation
- Bowing or deformity of the knee
- Inability to relieve pain with topical medication, oral medication, or physical therapy
How Many Types of Knee Osteoarthritis Surgery Are There?
Knee osteoarthritis surgery involving joint surface replacement—commonly known as knee replacement surgery—is a treatment that uses metal and high-quality materials to replace deteriorated joint surfaces. This helps restore knee movement to a state as close as possible to the original joint surface. Currently, knee replacement surgery is the most effective treatment for knee osteoarthritis and can restore a good quality of life for patients.
Knee surgery can be divided into two types:
Total Knee Replacement
Total knee arthroplasty (TKA) is a treatment for knee osteoarthritis that involves removing the entire original knee joint surface and replacing it with metal and high-quality materials. It is suitable for patients with severe knee osteoarthritis, multiple areas of joint degeneration, and significant knee deformity.
This method can address all problems associated with knee osteoarthritis, correct knee deformity, restore lost mobility, and reduce pain caused by joint surface wear, allowing patients to regain near-normal knee function.
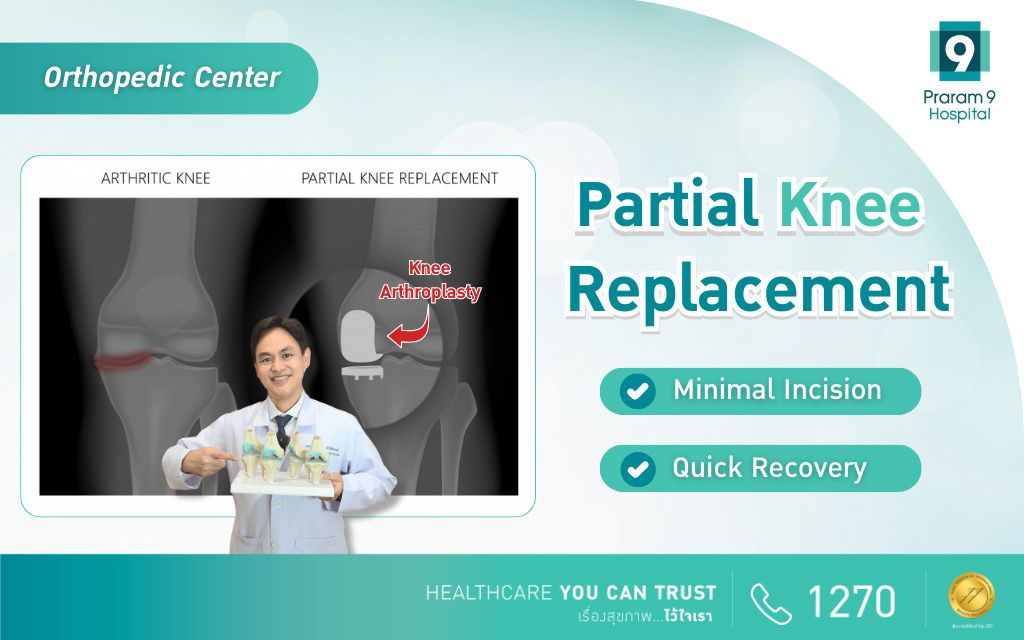
Partial Knee Replacement
Unicompartmental knee arthroplasty (UKA) is another treatment option for knee osteoarthritis, suitable for early stages when joint damage is localized. The procedure targets only the worn portion of the knee joint, removing the damaged surface and replacing it with metal and high-quality materials, while preserving the healthy joint surfaces—similar to filling a cavity in a tooth.
Partial knee replacement is suitable for patients with localized knee degeneration. Because only part of the bone is removed and there is less damage to surrounding tissues compared to total knee replacement, recovery time is shorter, overall pain is less, and postoperative knee function is closer to normal.
Advantages and Limitations of Knee Replacement Surgery
Knee osteoarthritis significantly affects patients’ quality of life, especially in severe cases. Currently, the most effective treatment is knee replacement surgery, which has the following advantages and limitations:
Advantages
- Reduces pain caused by bone-on-bone contact
- Restores joint movement and reduces joint stiffness
- Corrects joint deformity, allowing the knee to bear weight properly
- Reduces risks associated with knee osteoarthritis
- Long-lasting results, with a lifespan of more than 15 years in cases of total joint replacement
Disadvantages (Limitations)
- Not recommended for patients who have had a knee joint infection within the past 6 months
- Not suitable for patients with muscle weakness or bedridden patients
- Not recommended for patients who are unable to undergo physical therapy
Knee osteoarthritis significantly affects patients’ quality of life, especially in severe cases. Currently, the most effective treatment is knee replacement surgery, which has the following advantages and limitations:
Advantages of Knee Replacement Surgery
- Reduces pain caused by bone-on-bone contact
- Reduces joint stiffness caused by bone spurs and restores joint movement
- Corrects joint deformities and improves weight-bearing function
- Reduces risks associated with knee osteoarthritis, such as degeneration of nearby joints and diseases caused by reduced mobility
- Long implant lifespan; reports show that more than 90% of total knee replacements last longer than 15 years
Limitations of Knee Replacement Surgery
- Not suitable for patients with a knee joint infection within the past 6 months or those with severe muscle weakness
- May not be suitable for patients who have been immobile for a long time, such as bedridden patients, or those unable to communicate or cooperate with physical therapy
Preparation Before Knee Replacement Surgery
Proper preparation helps increase the chances of a smooth surgical process. Prior to surgery, staff will explain the preparation steps as follows:
Physical Preparation
- Stop all medications and supplements, especially herbal medicines; inform the doctor about any prescribed medications for individual assessment
- Stop smoking and drinking alcohol
- Maintain good health and avoid infections before surgery, such as dental checkups and blood sugar control in diabetic patients
- Refrain from eating and drinking for the period specified by the doctor
Preparing the Home for Postoperative Recovery
In addition to physical preparation, preparing the home environment is important to support recovery after surgery. Recommended preparations include:
- Clear walkways and remove obstacles; ensure floors are level to reduce fall risk
- Ensure adequate lighting throughout the home
- Install grab bars in the bathroom and near the toilet
- Place a chair in the bathroom to assist with showering
- If possible, arrange sleeping accommodations on the ground floor
Knee Replacement Surgery Procedure
The steps involved in knee replacement surgery include:
- An anesthesiologist administers anesthesia, either general anesthesia or spinal anesthesia
- The surgeon makes an incision approximately 12–15 cm long, depending on knee size, to expose the damaged joint surface
- The deteriorated joint surface is removed; the thickness and area depend on the severity of wear
- The knee prosthesis is implanted; material selection is based on clinical suitability
- Ligaments around the knee may be adjusted to restore proper alignment and improve weight distribution
The surgery typically takes 90–120 minutes. The patient is then monitored in the recovery room for 1–2 hours before being transferred to a patient room if stable.
Postoperative Care After Knee Replacement Surgery
After surgery, patients should follow medical advice, including:
- Elevating the knee with a pillow to reduce swelling and pain
- Regularly moving the ankle up and down to promote blood circulation
- Applying cold compresses as needed to reduce swelling
- Participating in rehabilitation and mobility training; initially guided by a physical therapist or physician, including muscle strengthening, weight-bearing training, and walking with a walker, as well as home exercise instruction
- Once walking with a walker is stable and confident, patients may be discharged home at the doctor’s discretion
Complications of Knee Replacement Surgery
With modern medical technology, knee replacement surgery is safer than ever. However, all surgeries carry risks. Possible complications include:
- Infection
- Deep vein thrombosis
- Injury to major blood vessels or nerves
- Joint stiffness or instability after surgery
- Postoperative pain
Serious complications such as infection are rare, occurring in less than 2% of patients worldwide. Deep vein thrombosis is more common due to reduced mobility after surgery, but standardized pre- and postoperative care can significantly reduce this risk. Joint stiffness or instability is uncommon and can be further reduced through computer-assisted or robot-assisted surgery.
Knee Osteoarthritis Surgery for Greater Mobility At the Joint Care Center, Praram 9 Hospital
Knee osteoarthritis no longer needs to limit daily life. Knee replacement surgery can effectively address knee osteoarthritis and restore quality of life. At the Joint Care Center, Praram 9 Hospital, we prioritize patient quality of life, providing knee replacement surgery by specialist physicians with comprehensive care from diagnosis through full recovery and return to daily activities.
For More Information
- Facebook : Praram 9 hospital
- Line : @Praram9Hospital
- Tel. 1270
Frequently Asked Questions About Knee Osteoarthritis Surgery
How many days of recovery are needed after knee osteoarthritis surgery?
Most patients can begin weight-bearing with assistive devices within 1 day after surgery. Many can walk to the bathroom independently early on and continue improving, with significant functional recovery within 3–6 months, depending on preoperative condition.
How long does a knee prosthesis last?
This depends on postoperative activity levels. Generally, knee prostheses last 15–20 years. Heavy use, accidents, or infections can shorten implant lifespan.
Revision surgery may be required in cases of surgical misalignment, joint instability, or stiffness. These risks can be reduced with computer-assisted or robot-assisted surgery.
References
Benjamin Ma, C. (2024, August 27). Knee joint replacement. MedlinePlus.https://medlineplus.gov/ency/article/002974.htm
Mayo Clinic Staff. (2024, November 15). Knee replacement. Mayo Clinic. https://www.mayoclinic.org/tests-procedures/knee-replacement/about/pac-20385276
Total Knee Replacement. (2024, February). OrthoInfo. https://orthoinfo.aaos.org/en/treatment/total-knee-replacement/
Chaiyakit, P. Hongku, N & Meknavin, S. (2009). A comparison of early clinical outcomes between computer assisted surgery and conventional technique in minimally invasive total knee arthroplasty. J Med Assoc Thai. 92-S6(S91-96). www.jmatonline.com/PDF/92-S6-PB-S91-S96.pdf