Health Articles
Knowledge
Diabetic Treatment
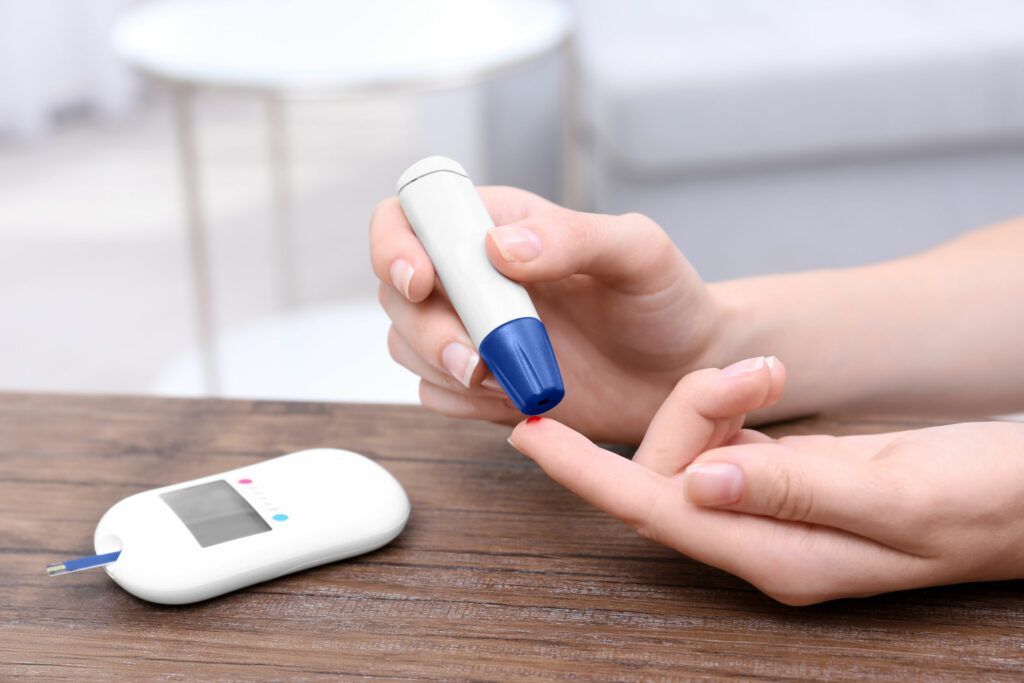

Diabetes is the chronic condition of high blood sugar that comes from a deficiency in producing insulin or function of insulin or both cases. Diabetes often involves many serious complications and can be the cause of premature death. However, diabetic patients can take care of themselves to reduce the risk of incidence.
The objective of treatment is to maintain the blood sugar to be similar to normal levels at all times. The training for management and self-care is an important part for diabetic treatment. The method of treatment depends on each part. The aspects of medical, psychosocial, and lifestyle of the patient are also used in the treatment.
– Treatment of Type 1 Diabetes Because the pancreas cannot produce the insulin, Type 1 Diabetes is difficult to control. Therefore, many treatment criteria are needed. For example: Control the diet carefully, plan the exercise, self-fasting blood sugar, and Metered Dose Inhale (MDI).
– Treatment of Type 2 Diabetes The treatment methods are diet control, exercise, and self-fasting blood sugar. In some cases, treatment method by oral medication and/or insulin injection might be needed. About 40% of patients with Type 2 Diabetes need to have insulin injection.